FAQ
What is compressed natural gas (CNG)?
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fossil fuel comprised mostly of methane, which is one of the cleanest, safest, burning alternative fuels available for vehicles. CNG is not a widely used type of transportation fuel in the U.S. However, the demand for CNG in the U.S. has grown this past year.
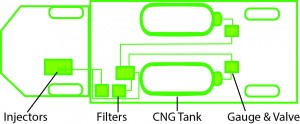
CNG Compatible Vehicles- Natural Gas Vehicles (NGV)
- 9 million natural gas vehicles worldwide and 120,000 in the U.S.
- Only one consumer CNG compatible car is on the market, The Honda Civic GX.
- Typical Natural Gas Vehicles (NGV) include; taxi cabs, over-the-road trucks, street sweepers, ice resurfacers, transit buses, refuse haulers, school buses, delivery vehicles , airport shuttle, and forklifts.
Availability/sources
CNG can be collected from both onshore and offshore wells. US domestic production has boomed out of shale deposits along the Gulf.
What are the key benefits of CNG?
Price
CNG is typically 1/3 less than petroleum based fuel. It is also less volatile than the petroleum market.
Example: with an average of $2.15 a gas gallon equivalent, a CNG driver will cut their fuel costs in half.
Emissions Reduction
Lower emissions than regular petroleum fuel but the same energy output.
Fueling with CNG can reduce exhaust emissions of:
- Carbon monoxide (CO) by 75 percent
- Non-methane organic gas (NMOG) by 87 percent
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) by 87 percent
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) by almost 25 percent below those of gasoline vehicles
Vehicle Differences
A quieter operating vehicle with a great performance.
Watch this short video made by our partner Waste Management: